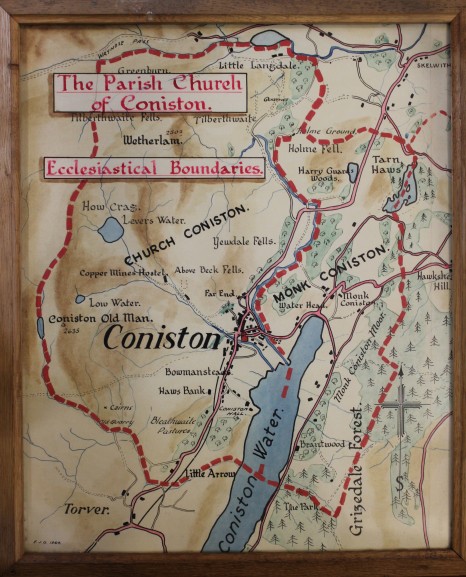
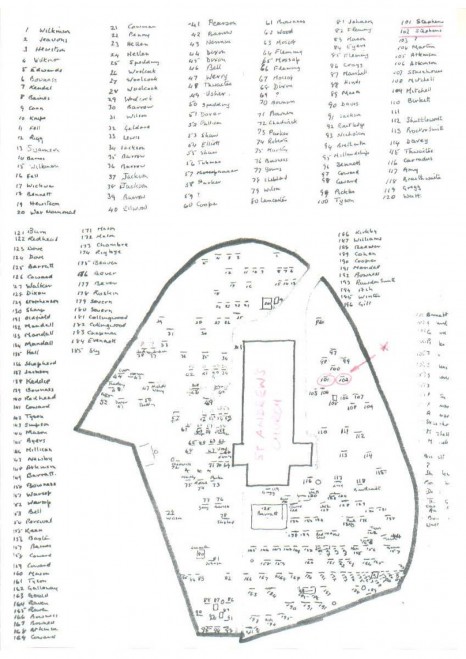
Walking around the church grounds, one step after another is fluffily soft; feeling microorganisms living underneath. Someone mentioned that perhaps a graveyard is the most nutritious and healthy environment to grow plants, on which no one has spread chemical pesticides. Sometime in the 16th century, the cemetery of St. Andrews church in Coniston, England was established to accommodate the practice of burying dead bodies. No records of death were kept, and it was long before the current church was constructed in 1819. According to the vicar Mark East, the first appearance of gravestones was around this time; in order for the family of the deceased to express wealth and living history, a visualization of death was constructed and carried on as a conventional wisdom.
“There is no wealth but life,” were the words of John Ruskin, the great thinker and early pioneer of ecology, who from 1900, the year of his death, also sleeps at grave #172 at St. Andrews church. He had spent his later years in Brantwood, his house overlooking Coniston Water. During this period, he published a monthly series called “Fors Clavigera: Letters to the Workmen and Labourers of Great Britain”, which took a form equivalent to the Blog in today’s terms, predicting the effects of industrialization on the natural world, and devoting his writing to his social reform crusade.
Although the issue of social inequality was addressed to the factory workers around the time of the Industrial Revolution in Britain, it hits a sore spot in current society. Coniston presently engages with tourism on industrial scales: the town is surrounded by nature, and 40% of the local population is composed of holiday homes; sheep farmers are subsidized by the government to maintain heritage varieties; people are generally “well-off”, so consequently isolation in one’s own individual interests cuts off engagement in village culture, and it interferes in local food production and distribution. In this context, small local farmers went into bankruptcy because of the price control of multi-national corporations, better able to service the high turn-over rate of tourism. Urban agriculture and the allotment system are very popular community models elsewhere in England, but in a place like Coniston they are not the custom.
Well then, how can we (artists) revitalize the idea of village food production, and maybe thereby revitalize the village? Together with Grizedale Arts, we proposed to the Church Council of Coniston the idea of growing vegetables on John Ruskin’s grave at St. Andrews Church.
“…six feet square, if no more can be had, — nay, the size of a grave, if you will, but buy it freehold, and make a garden of it, by hand-labour ; a garden visible to all men, and cultivated for all men of that place. If absolutely nothing will grow in it, then have herbs carried there in pots…” (John Ruskin 1874).
Taking his words seriously, this project is more symbolic rather than provocative, by growing food by hand to enrich the village with a group of locals.
to be continued…
///////////////////////////////////////////////
Grizedale Arts is a residency organization based on a farm in the centre of the Lake District in England. It tries to develop the way art thinking and art practice impact on society, through projects, exhibitions and events developed through an extended community of artists and creative people associated with it. Emi Uemura is a resident artist for Grizedale Arts 2011.

 时间 posted on: 11 August 2011 |
时间 posted on: 11 August 2011 |  发布者 author:
发布者 author: 
 分类 filed under:
分类 filed under: